– DC motor
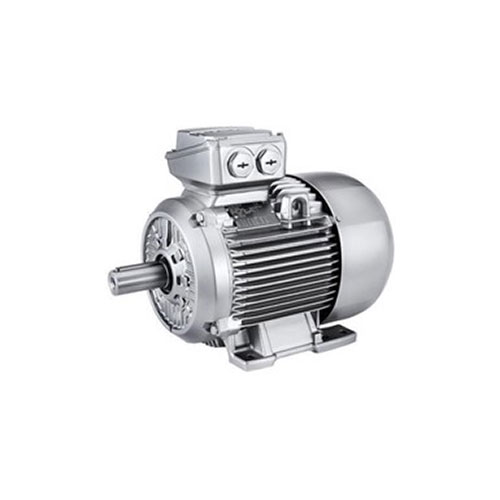
A DC motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. In a DC motor, the input electrical energy is the direct current which is transformed into the mechanical rotation.
– AC motor
An AC motor is an electric motor driven by an alternating current (AC). The AC motor commonly consists of two basic parts, an outside stator having coils supplied with alternating current to produce a rotating magnetic field, and an inside rotor attached to the output shaft producing a second rotating magnetic field. The rotor magnetic field may be produced by permanent magnets, reluctance saliency, or DC or AC electrical windings.
– Induction motor
An induction motor or asynchronous motor is an AC electric motor in which the electric current in the rotor needed to produce torque is obtained by electromagnetic induction from the magnetic field of the stator winding. An induction motor can therefore be made without electrical connections to the rotor.
– Synchronous AC electric motor
A synchronous electric motor is an AC electric motor in which, at steady state, the rotation of the shaft is synchronized with the frequency of the supply current; the rotation period is exactly equal to an integral number of AC cycles.
– Asynchronous AC electric motor
An asynchronous motor is an alternating current (AC) electric motor that utilizes an induced current in its rotor rather than a physical power supply to produce its rotational motion. Most electric motors rotate as a result of the interaction between the electromagnetic fields created in the stator and rotor of the motor.





















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.